News
Wire-Friendly Domain-Specific Processor for Angstrom-Era Nodes with High Core Density
A new paper from researchers at Politecnico di Torino and imec presents a domain-specific processor architecture aimed at machine learning applications. The design improves interconnect efficiency with reduced wire length and heightened core density, achieving more than 3x higher density than current state-of-the-art processors. This architecture is a promising solution for next-generation designs, showcasing minimal manual layout intervention for physical efficiency.
Launches
Thermally-Aware Multi-Objective Scheduling Framework for DL Workloads on Heterogeneous Multi-Chiplet PIM Architectures
Researchers from the University of Wisconsin–Madison have introduced THERMOS, a novel scheduling framework for AI workloads on heterogeneous multi-chiplet architectures. The framework employs reinforcement learning to optimize execution time and energy consumption, achieving up to 89% faster performance compared to existing algorithms, while maintaining minimal overhead.
Charts
Scheduling Architecture Integrated With M3D BEOL Memories For LLM Inference
A study from Georgia Tech and Samsung presents a scheduling architecture designed to enhance long-context large language model inference. The architectural optimizations achieve significant performance improvements, including 8.06x decode speedup and reduced latency, addressing the bottlenecks associated with high bandwidth memory.

Research
Energy-Accuracy Trade-Offs in Massive MIMO Signal Detection Using SRAM-Based IMCs
Research from the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign dives into energy-efficient signal detection for massive MIMO systems using SRAM-based in-memory computing architectures. The study explores the balance between energy consumption and accuracy, showcasing how IMC-based detectors can outperform conventional designs while meeting stringent accuracy requirements.

Insight
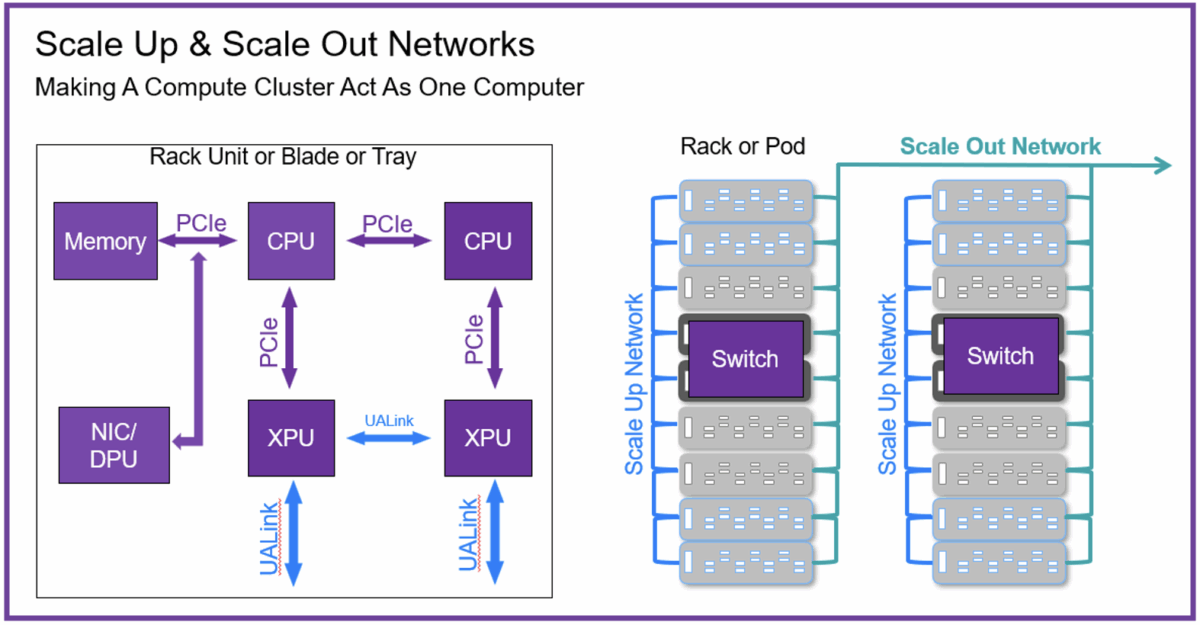
Synopsys Enables AI Advances with UALink
In a recent discussion, Synopsys’ industry experts outlined the transformative impact of the UALink standard on AI infrastructure. The open specification improves die-to-die communication among AI accelerators, addressing critical design challenges in hyperscale data centers. Insights from the panel highlight the collaborative efforts of over 100 companies in advancing AI technology and optimizing memory access.
Thank you for staying with us for the latest news in the semiconductor industry. We look forward to bringing you more updates and insights into emerging technologies and innovations in the field.
