News
A crisis at chipmaker Nexperia sent automakers scrambling
A geopolitical dispute involving Chinese-owned Dutch chipmaker Nexperia has disrupted the global automotive supply chain. The Dutch government invoked a rarely used law to assert control over Nexperia due to national security concerns, leading to the ousting of its Chinese CEO. In response, China blocked exports of Nexperia chips from its Dongguan plant, severely impacting automakers like Honda, Ford, General Motors, Nissan, and Mercedes-Benz, who rely on Nexperia’s discrete chips for essential vehicle functions.
- Dutch government asserted control over Nexperia, citing national security and “governance shortcomings.”
- China retaliated by blocking chip exports from Nexperia’s Chinese factory, causing major disruptions for global automakers.
- The crisis highlights semiconductor supply chain vulnerabilities and the impact of geopolitical tensions on critical industries.

Launches
Eta Compute Rebrands as ModelCat, Unveils Agentic Model Builder
AI software startup Eta Compute has rebranded as ModelCat and launched a new hardware-aware model building platform for edge devices, leveraging agentic AI. This platform uses an AI agent to automate the creation of models tailored to specific edge hardware constraints, significantly reducing the manual effort in the development cycle. ModelCat has partnered with NXP to integrate a dedicated version of the tool into NXP’s eIQ software ecosystem, and its cloud platform supports various edge hardware from NXP, STMicroelectronics, Silicon Labs, Qualcomm, and others for real-world testing.
- ModelCat’s platform uses agentic AI to automate hardware-aware model creation for edge devices.
- The tool significantly reduces development time by testing models on real hardware in the cloud.
- Partnership with NXP extends its reach into the eIQ software ecosystem for NXP hardware targets.

Charts
Omdia: Display Glass Revenue Reached a Record High of JPY 270 Billion in 3Q 2025
According to Omdia, display glass revenue hit a record JPY 270 billion in Q3 2025, marking a 5% quarter-over-quarter and 14% year-over-year increase. This growth is driven by both increased prices and demand, reflecting a strategic shift by major glass makers towards profitability after a decade of intense competition. Since 2022, prices have risen over 25% as companies manage production capacity and avoid new tank investments, focusing instead on efficiency. Chinese glass makers, however, continue aggressive investments, particularly in G8.5 glass tanks, and are expected to gain market share long-term. Major glass makers are also exploring new business areas, including glass for the semiconductor industry (TGV, support glass).
![]()
Research
Predicting Stochastic EUV Defect Density with Electron Noise and Resist Blur Models
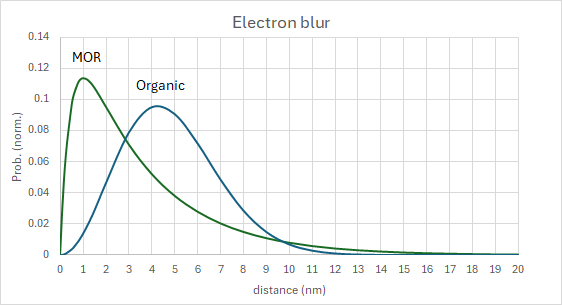
New research explores the impact of secondary electron noise on defect probability in Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, utilizing updated blur models for chemically amplified (CAR) and metal oxide (MOR) resists. The study highlights that resist blur significantly degrades contrast, affecting defect probability calculations. It reveals that EUV exposures are exponentially more defective than ArF immersion lithography, with edge defects being the most likely due to proximity to feature edges. As lithography pitches shrink, resist blur and electron noise are becoming more critical than optical parameters, indicating the growing necessity for advanced techniques like multipatterning to manage defectivity in future semiconductor manufacturing.
- Secondary electron noise and resist blur are key factors in EUV lithography defect probability.
- EUV exposures exhibit exponentially higher defectivity compared to ArF immersion.
- As pitches shrink, resist blur and electron noise are now more critical than optical parameters, necessitating advanced patterning.
Insight
Moving AI Workloads To The Edge
Industry experts discussed the growing trend of moving AI workloads from the cloud to the edge, driven by crucial factors such as consistent performance, reduced network reliance, lower cloud computing costs, and enhanced data privacy. The panel emphasized that while AI training remains compute-intensive in the cloud, inference is increasingly shifting to edge devices like phones, wearables, and autonomous vehicles, utilizing specialized NPUs and TPUs. This shift also addresses security concerns by keeping sensitive data localized, vital for corporate IP and applications where latency is critical, such as autonomous driving and security monitoring. The discussion highlighted a hybrid model where cloud and edge solutions complement each other, with edge AI enabling new, efficient, and secure user experiences.
- Key drivers for edge AI include consistent performance, privacy, reduced latency, and lower cloud costs.
- Edge devices are increasingly handling AI inference with specialized NPUs and TPUs.
- Hybrid cloud-edge models are emerging, enabling new applications and enhancing security for sensitive data.

Stay tuned for more essential updates as the semiconductor industry continues to innovate and adapt to evolving technological demands.
